Total knee replacement (TKR) surgery is a transformative procedure for patients suffering from severe knee arthritis or injury. Among the various surgical techniques, the subvastus approach, Quadriceps Sparing Approach, stands out as a minimally invasive option that avoids cutting muscles or tendons, leading to faster recovery and improved outcomes.
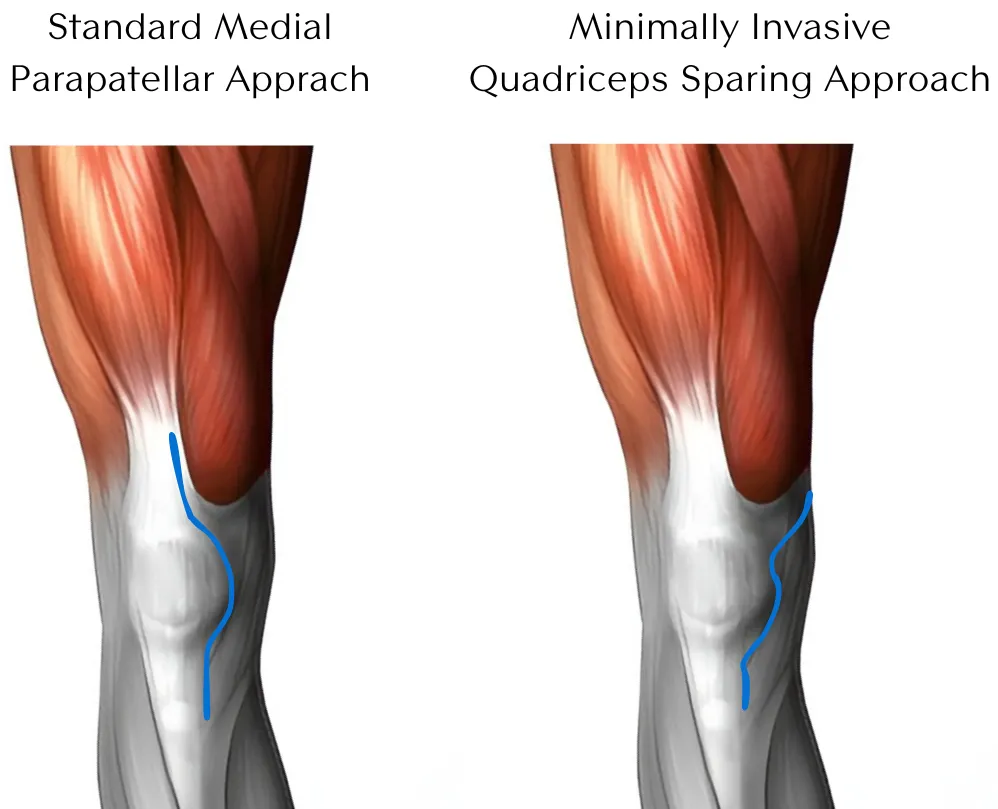
Medial Parapatellar Approach
The medial parapatellar approach is a traditional technique that involves an incision along the medial border of the patella and the quadriceps tendon, extending around the patella to the tibial tubercle. While this approach offers excellent exposure of the knee joint, it involves cutting through the vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) muscle attachment to the kneecap, which can affect postoperative quadriceps strength and recovery time.
Key Points:
- Exposure: Provides excellent joint visibility, beneficial for complex cases.
- Muscle Involvement: Involves cutting the VMO muscle attachment to the patella, potentially slowing recovery.
- Postoperative Considerations: Patients may experience slower recovery of quadriceps function due to muscle dissection.
Subvastus Approach
The subvastus approach also known as the “Quadriceps Sparing Approach”, is a muscle-sparing technique designed to minimize damage to the quadriceps muscle group. This approach involves making an incision below the vastus medialis muscle without cutting through it, preserving the muscle’s integrity.
Key Points:
- Minimally Invasive: Spares the quadriceps muscle and tendon, leading to less trauma and faster recovery.
- Faster Recovery: Patients often experience quicker recovery of quadriceps function, less postoperative pain, and greater early knee flexion.
- Postoperative Considerations: Ideal for patients prioritizing rapid rehabilitation and muscle preservation.

Recent Studies
Studies have highlighted the benefits of the subvastus approach. These studies show that patients undergoing the subvastus technique have faster recovery times, less pain, and better early knee flexion compared to those who undergo the medial parapatellar approach. 1, 2
Conclusion
Both the subvastus and medial parapatellar approaches have their respective benefits and limitations. However, the subvastus approach’s minimally invasive nature, which avoids cutting muscles or tendons, makes it a superior option for many patients undergoing TKR. This approach not only leads to faster recovery and less pain but also enhances overall patient satisfaction, marking it as the cutting edge in knee replacement surgery. Ask your knee replacement surgeon about the approach that they intend to use.
References
- Khan MNH, Abbas K, Faraz A, Ilyas MW, Shafique H, Jamshed MH, Hashmi P. Total knee replacement: A comparison of the subvastus and medial parapatellar approaches. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Aug 8;68:102670. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102670. PMID: 34408867; PMCID: PMC8361225.
- Roysam GS, Oakley MJ. Subvastus approach for total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, and observer-blinded trial. J Arthroplasty. 2001 Jun;16(4):454-7. doi: 10.1054/arth.2001.22388. PMID: 11402407.




