Talk with Dr. Morton about Robotic Hip Replacements
Talk with Dr. Morton about Robotic Hip Replacements
- Board-certified, Fellowship Trained Surgeon in Robotic Hip Replacements
- First Robotic Hip Replacement Performed in Hawaii by Dr. Morton
- Anterior Hip Replacement Expert – Soft tissue sparing, smaller incisions
- Robotic-Assistance – More accurate implant positioning
- No Posterior Hip Precautions – The traditional approaches require patients to avoid internally rotating the hip, or bending the hip past 90 degrees. This can be very limiting for patients during their recovery phase.
- Faster and Easier Recovery – Without posterior hip precautions and less pain after surgery, recovery is much faster
- Most Surgeries Are Same-Day, Outpatient surgeries– Many patients are able to go home on the day of surgery
- Lower Risk of Hip Dislocation – More accurate positioning of implants during surgery allow for a lower risk of hip dislocation
- Equal Leg Lengths – Leg length discrepancy after surgery, especially in Hawaii (where people wear slippers or walk barefoot on the beach), can be a big deal. Intra-operative x-rays performed during the anterior hip surgery allow for more accurate placement of implants and avoid leg length issues.
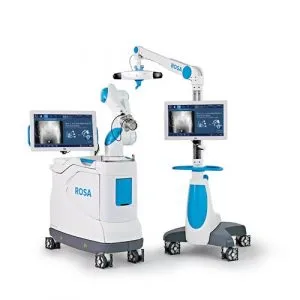
Robotic Hip Replacement
Robotic-Assisted Anterior Hip Replacement with Rosa is a new system that provides many advantages over traditional approaches.
Advantages to the Rosa robotic hip replacement system include:
- Minimally invasive techniques with smaller incisions
- Robotic system designed to use the Anterior approach
- Improved accuracy of component positioning
- Lower risk of hip dislocation
- Efficient system, lower operating room time
- Accelerated recovery time due to minimal trauma to muscles, tendons, and nerves
- Patient-specific planning
- Lower radiation exposure
- Designed specifically for the Anterior Approach
Anyone who is a candidate for a hip replacement is a candidate for a robotic hip replacement. It is not limited to any age group or type of patient.

Who is a Candidate for a Robotic Hip Replacement?
You may be a candidate for a hip replacement if you have experienced:
- Pain that prevents you from sleeping
- Pain or Stiffness after a long period of sitting
- Hip pain limiting you from the activities that you love
- Difficulty getting up from a seated position or climbing in and out of a bathtub
You may want to discuss some non-operative treatment strategies with your doctor before proceeding. When non-operative treatment fails, you may be a candidate for a hip replacement.
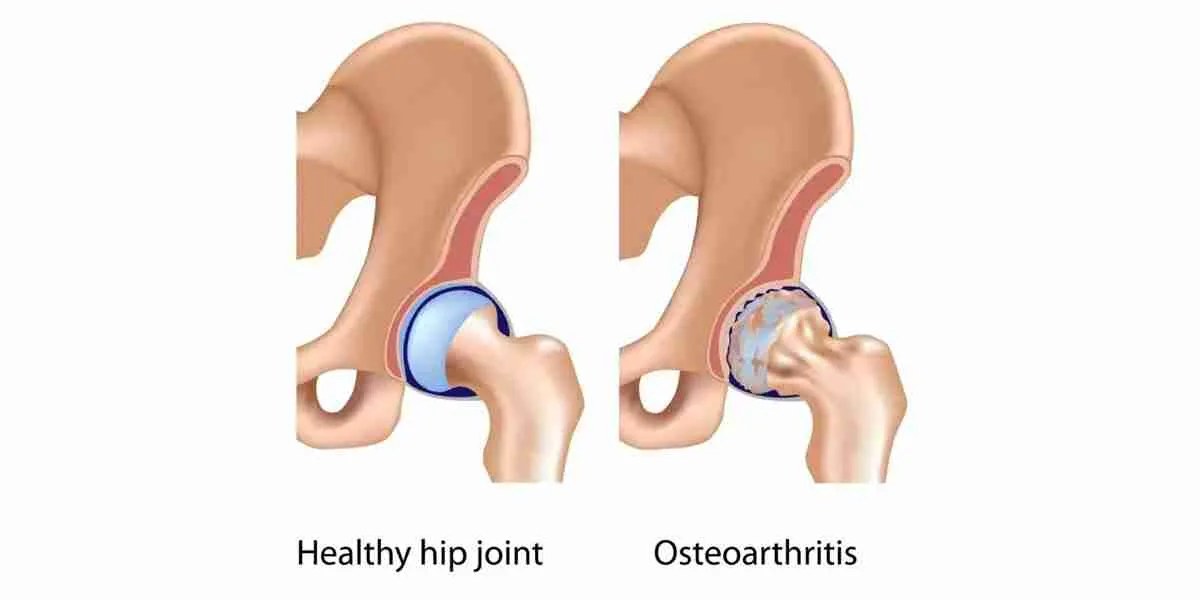
Hip osteoarthritis is the most common cause of hip pain. Osteoarthritis is the wear and tear of the cartilage around the joint. Cartilage in the joint is the smooth protective surface on the ends of the bone that prevents the bone from rubbing together. Once the cartilage is worn away, the ends of the bone rub together and this can become painful. Often, basic activities such as walking, sitting, and even laying down can become painful.
Other causes of hip pain include osteonecrosis (loss of blood supply to the hip joint, causing dead bone), trauma, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Minimally Invasive Approach
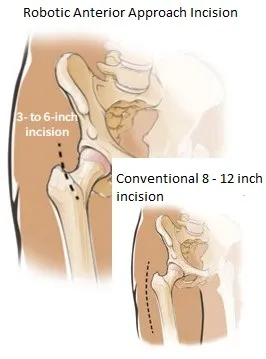
The Rosa Hip Replacement approach is a minimally invasive procedure that takes advantage of the anterior approach utilizing a 3-to-6 inch incision in the front of the leg directly over the hip joint, compared to the traditional 8-to-12 inch incision on the side.
In addition, this approach allows the preservation of your muscles and soft tissue without detaching any of the muscles as in some of the traditional approaches. This approach helps with the faster recovery time following hip replacement surgery.
- Soft Tissue Sparing – Anterior approach avoids cutting the muscle, as it follows the natural path between the muscles.
- Smaller Incisions – Anterior approach to the hip is much closer to the hip joint, allowing for a smaller incision.
- Less Pain – Many patients do complain of pain on the day of surgery, and may not require more than Tylenol for pain control.
- No Posterior Hip Precautions – The traditional approaches require patients to avoid internally rotating the hip, or bending the hip past 90 degrees. This can be very limiting for patients during their recovery phase.
- Faster and Easier Recovery – Without posterior hip precautions and less pain after surgery, recovery is much faster
- Early Discharge From Hospital – Many patients are able to go home on the day of surgery
- Lower Risk of Hip Dislocation – More accurate positioning of implants during surgery allow for a lower risk of hip dislocation
- Equal Leg Lengths – Leg length discrepancy after surgery, especially in Hawaii (where people wear slippers or walk barefoot on the beach), can be a big deal. Intra-operative x-rays performed during the anterior hip surgery allow for more accurate placement of implants and avoid leg length issues.
- No CT-scan or pins – Unlike many other robotic hip platforms, no CT scan or extra-incisional pin sites are required to perform a robotic total hip.
- Anterior Hip Benefit – Designed specifically for the Anterior Approach
Advantages of Using a Robot During Your Hip Replacement
A survey in 2016 evaluated perceptions about robotic-assisted surgery: 72% of respondents felt that robotic-assisted surgery is Faster, Safer, Less Painful or Provided Better Results than conventional minimally invasive surgery.
- Boys, J. A., Alicuben, E. T., DeMeester, M. J., Worrell, S. G., Oh, D.S., Hagen, J. A., & DeMeester, S. R. (2016). Public perceptions on robotic surgery, hospitals with robots, and surgeons that use them. Surgical endoscopy, 30(4), 1310–1316. 2016.
Several studies demonstrate improved patient-reported outcomes following Robotic Hip Replacement vs Conventional Hip Replacements
- Clement ND, Gaston P, Bell A, et al. Robotic arm-assisted versus manual total hip arthroplasty. Bone & Joint Research. 2021 Jan;10(1):22-30. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.101.bjr-2020-0161.r1. PMID: 33380216; PMCID: PMC7845457.
- Shibanuma N, Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Takayama K, Sanada Y, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R, Hayashi S. Early postoperative clinical recovery of robotic arm-assisted vs. image-based navigated Total hip Arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Mar 29;22(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04162-3. PMID: 33781263; PMCID: PMC8008585.
- Bukowski BR, Anderson P, Khlopas A, Chughtai M, Mont MA, Illgen RL 2nd. Improved Functional Outcomes with Robotic Compared with Manual Total Hip Arthroplasty. Surg Technol Int. 2016 Oct 26;29:303-308. PMID: 27728953.
- Ng N, Gaston P, Simpson PM, Macpherson GJ, Patton JT, Clement ND. Robotic arm-assisted versus manual total hip arthroplasty : a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Joint J. 2021 Jun;103-B(6):1009-1020. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B6.BJJ-2020-1856.R1. PMID: 34058875.
Hip Dislocation is one of the leading causes for revision and can increase hospital costs by up to 300% when compared to routine total hip replacement.
- Hailer N P, Weiss R J, Stark A, Kärrholm J. The risk of revision due to dislocation after total hip arthroplasty depends on surgical approach, femoral head size, sex, and primary diagnosis: an analysis of 78,098 operations in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop 2012; 83 (5): 442-8
- Kostensalo I, Junnila M, Virolainen P, Remes V, Matilainen M, Vahlberg T, Pulkkinen P, Eskelinen A, Mäkelä KT. Effect of femoral head size on risk of revision for dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: a population-based analysis of 42,379 primary procedures from the Finnish Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop 2013; 84 (4): 342-7
- Gwam CU, Mistry JB, Mohamed NS, Thomas M, Bigart KC, Mont MA, et al. Current epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States: National Inpatient Sample 2009 to 2013. J Arthroplasty 2017;32:2088e9
- Abdel MP, Cross MB, Yasen AT, Haddad FS. The functional and financial impact of isolated and recurrent dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J 2015;97:1046e9.
- Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital cost of dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 2006;88:290.
A 2021 study showed that 100% of hips studied with the Rosa Hip Platform are within the Lewinnek and Callanan Safe zones, reducing the chance for hip dislocation.
Compared to 73% performed with traditional instrumentation.
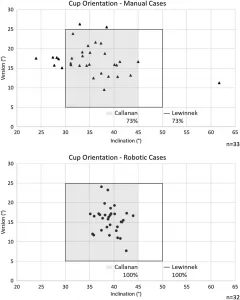
Scatterplots of traditional (top) vs robotic (bottom) cases within the Lewinnek and Callanan safe zones. The acetabular component orientation is reproducible (with fewer outliers) in the robotic group compared to the manual group (p=0.002), demonstrating improved accuracy of component positioning.
- Kamath AF, Durbhakula SM, Pickering T, Cafferky NL, Murray TG, Wind Jr. MA, Méthot S. Improved Accuracy and Fewer Outliers with a Novel CT-free Robotic THA System in Matchedpair Analysis with Manual THA. Journal of Robotic Surgery. 2021 Oct 28. doi: 10.1007/s11701-021-01315-3. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34709535
Advantages of Using a Robot During Your Hip Replacement
A survey in 2016 evaluated perceptions about robotic-assisted surgery: 72% of respondents felt that robotic-assisted surgery is Faster, Safer, Less Painful or Provided Better Results than conventional minimally invasive surgery.
- Boys, J. A., Alicuben, E. T., DeMeester, M. J., Worrell, S. G., Oh, D.S., Hagen, J. A., & DeMeester, S. R. (2016). Public perceptions on robotic surgery, hospitals with robots, and surgeons that use them. Surgical endoscopy, 30(4), 1310–1316. 2016.
Several studies demonstrate improved patient-reported outcomes following Robotic Hip Replacement vs Conventional Hip Replacements
- Clement ND, Gaston P, Bell A, et al. Robotic arm-assisted versus manual total hip arthroplasty. Bone & Joint Research. 2021 Jan;10(1):22-30. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.101.bjr-2020-0161.r1. PMID: 33380216; PMCID: PMC7845457.
- Shibanuma N, Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Takayama K, Sanada Y, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R, Hayashi S. Early postoperative clinical recovery of robotic arm-assisted vs. image-based navigated Total hip Arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Mar 29;22(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04162-3. PMID: 33781263; PMCID: PMC8008585.
- Bukowski BR, Anderson P, Khlopas A, Chughtai M, Mont MA, Illgen RL 2nd. Improved Functional Outcomes with Robotic Compared with Manual Total Hip Arthroplasty. Surg Technol Int. 2016 Oct 26;29:303-308. PMID: 27728953.
- Ng N, Gaston P, Simpson PM, Macpherson GJ, Patton JT, Clement ND. Robotic arm-assisted versus manual total hip arthroplasty : a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Joint J. 2021 Jun;103-B(6):1009-1020. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B6.BJJ-2020-1856.R1. PMID: 34058875.
Hip Dislocation is one of the leading causes for revision and can increase hospital costs by up to 300% when compared to routine total hip replacement.
- Hailer N P, Weiss R J, Stark A, Kärrholm J. The risk of revision due to dislocation after total hip arthroplasty depends on surgical approach, femoral head size, sex, and primary diagnosis: an analysis of 78,098 operations in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop 2012; 83 (5): 442-8
- Kostensalo I, Junnila M, Virolainen P, Remes V, Matilainen M, Vahlberg T, Pulkkinen P, Eskelinen A, Mäkelä KT. Effect of femoral head size on risk of revision for dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: a population-based analysis of 42,379 primary procedures from the Finnish Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop 2013; 84 (4): 342-7
- Gwam CU, Mistry JB, Mohamed NS, Thomas M, Bigart KC, Mont MA, et al. Current epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States: National Inpatient Sample 2009 to 2013. J Arthroplasty 2017;32:2088e9
- Abdel MP, Cross MB, Yasen AT, Haddad FS. The functional and financial impact of isolated and recurrent dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J 2015;97:1046e9.
- Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital cost of dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 2006;88:290.
A 2021 study showed that 100% of hips studied with the Rosa Hip Platform are within the Lewinnek and Callanan Safe zones, reducing the chance for hip dislocation.
Compared to 73% performed with traditional instrumentation.

Scatterplots of traditional (top) vs robotic (bottom) cases within the Lewinnek and Callanan safe zones. The acetabular component orientation is reproducible (with fewer outliers) in the robotic group compared to the manual group (p=0.002), demonstrating improved accuracy of component positioning.
- Kamath AF, Durbhakula SM, Pickering T, Cafferky NL, Murray TG, Wind Jr. MA, Méthot S. Improved Accuracy and Fewer Outliers with a Novel CT-free Robotic THA System in Matchedpair Analysis with Manual THA. Journal of Robotic Surgery. 2021 Oct 28. doi: 10.1007/s11701-021-01315-3. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34709535
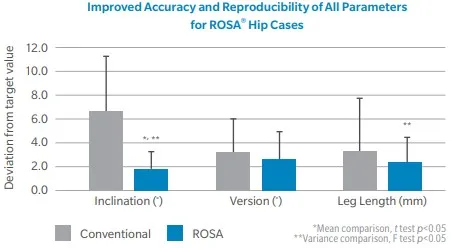
2021 Cadavaeric study comparing Rosa Hip to conventional instruments demonstrated:
- Component positioning significantly more accurate and more reproducible, with fewer outliers
- Leg length discrepancy significantly more reproducible, with fewer outliers (easier to achieve goal leg lengths following surgery)
- Kamath AF, Durbhakula SM, Pickering T, Cafferky NL, Murray TG, Wind Jr. MA, Méthot S. Improved Accuracy and Fewer Outliers with a Novel CT-free Robotic THA System in Matchedpair Analysis with Manual THA. Journal of Robotic Surgery. 2021 Oct 28. doi: 10.1007/s11701-021-01315-3. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34709535
Preparing for Your Robotic Hip Replacement Surgery
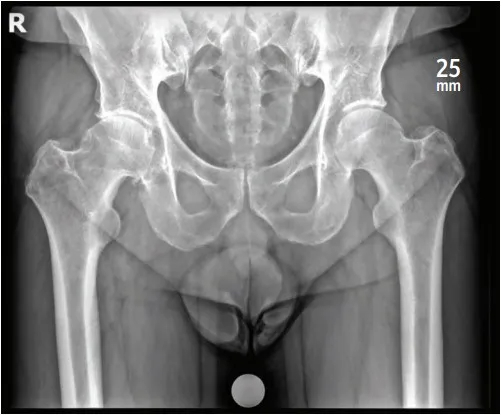
Prior to your surgery, you will get a set of xrays, including your pelvis and spine. The pelvis x-rays use a marker to help with preoperatively templating of your hip and measure the size and positioning of your implants.
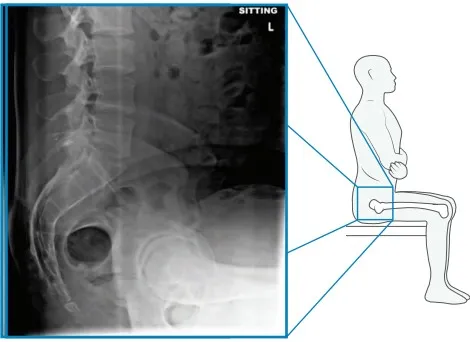
The spine x-rays will help us evaluate the pelvic-spine relationship. Osteoarthritis of the spine can sometimes change the functional anatomy of the hip. Understanding this relationship helps us to better position your implants.

Surgical Approach
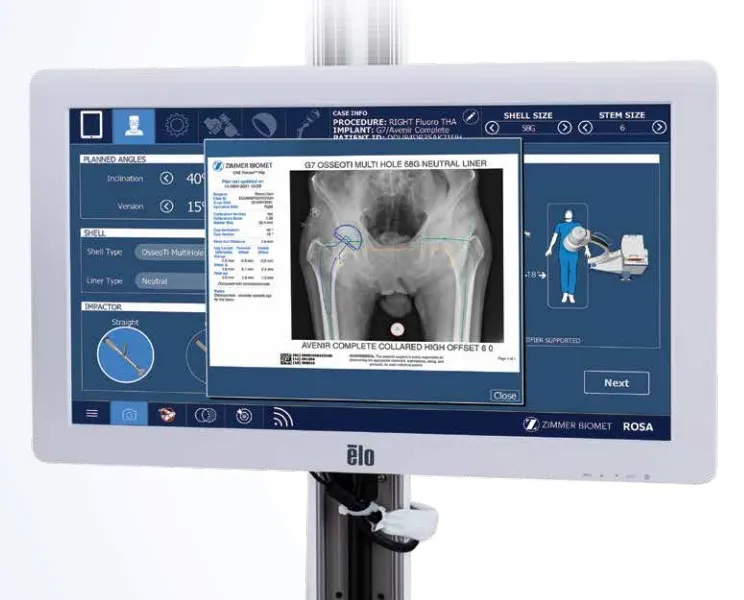
Patient-specific planning
Before your surgery, ever hip is planned to the appropriate size for the stem and cup.
Surgical Approach
The surgical approach for the Rosa robotic-assisted hip replacement is similar to that of an Anterior Hip Approach. Superficially, the dissection is between the sartorius and tensor fascia lata muscles. The deep dissection goes between the rectus femoris and gluteus medius muscles. In this way, the muscles are not cut, allowing for a faster recovery.
Robotic Accuracy and Control
After the femoral head is removed and the pelvis is prepared for cup implantation, ROSA is used to guide the implant into the correct position.
This enables the cup to be accurately placed with guidance from the robotic assistance.
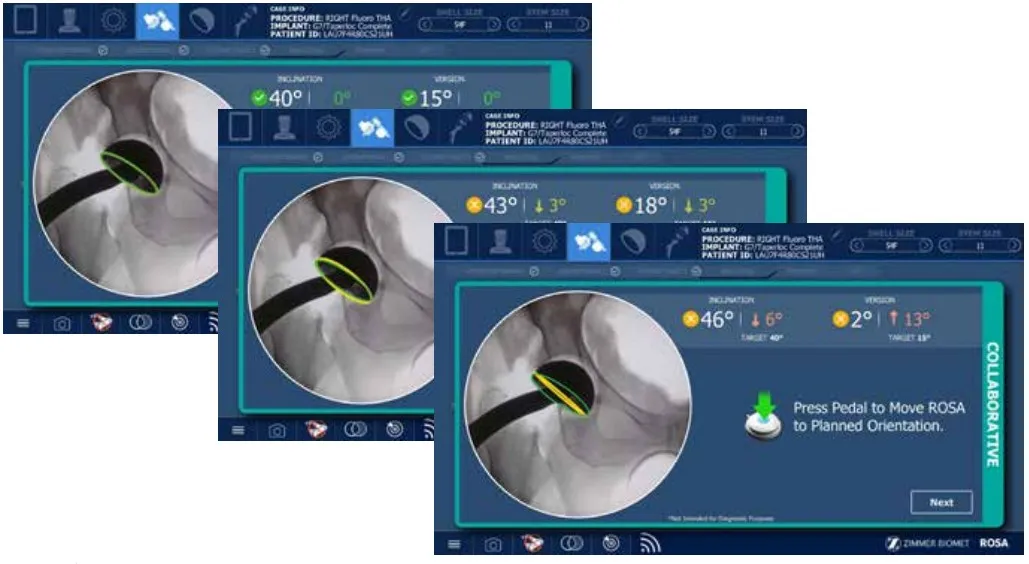
Controlled Impaction
The cup is then impacted in the desired position while attached to Rosa. The position is typically based on Lewinnek and Callanan safe zones. This position can be altered based on your preoperative spine x-rays.

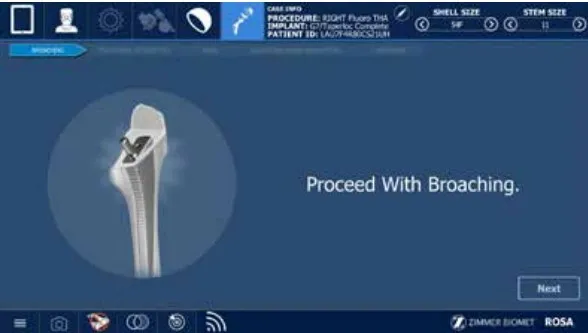
Stem Placement
The stem is then broached and temporary sized by hand.
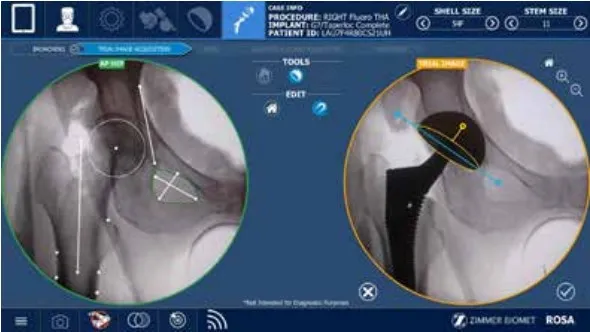
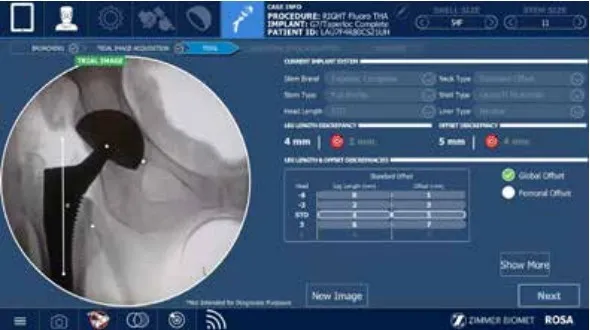
Confirmation of Appropriate Size with Computer Navigation
After the stem has been sized. The rosa computer will help determine if leg lengths and offset will be matched appropriately. The Rosa robotic system returns information on implant positioning in a way not available via conventional total hip replacement.
Traditionally, many patients after the posterior total hip replacement complained of leg length inequality and pain to the outside of their hip.
Sometimes getting equal leg lengths obtained perfectly and can be harder to achieve during revision and deformity surgery.
During surgery, Dr. Morton also considers the offset of your hip. Offset is the measurement of how far your femur bone is from your pelvis bone. The further away it is, the higher the offset. A high offset can sometimes put increased pressure on the IT band and cause pain. A low offset can cause an unstable hip.
Recovery
Once your final implant has been placed, you’re on the road to recovery!
Rest easy knowing that your hip has been placed with the latest technology and modern techniques.

Recovery from Your Robotic Hip Replacement
When deciding to have a hip replacement, you need to understand the limitations of your joint replacement surgery. Over 90% of people who have a total hip replacement have an incredible reduction in their hip pain and a dramatic improvement in returning to a better function. For most patients with normal use and activity, the hip replacement rarely wears out the plastic spacer. Dr. Morton likes to follow up with his patients on an annual basis with an x-ray to ensure that your hip replacement is continuing to function at the best of its ability. Increased activity or weight may speed up the wear and tear on your plastic components and may cause the hip replacement to loosen or become painful. After your recovery, you will feel like you can do many physical activities. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons advises our patients to avoid running, jogging, jumping, or other high-impact activities with a hip replacement.
Consider the Risks Before Surgery
Summary
Robotic-Assisted Anterior Hip Replacements is a tremendous advancement in the world of hip reconstruction surgery. This soft-tissue sparing procedure allows for more accurate component positioning, faster recovery, and a lower risk of complications. Schedule your appointment with Dr. Morton today!
Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Pain (FAQ)
Long-distance travel should usually be avoided until at least after your initial post-operative visit with your surgeon. The concern with long-distance travel is the possibility of the development of a blood clot, or missing a postoperative complication.
Once you are on a long trip, Dr. Morton recommends that you get up to stretch or walk at least once per hour during a long trip. Taking 81mg of aspirin daily is a useful adjunct. Dr. Morton recommends starting aspirin 2 days before your trip, and 2 days after your trip to avoid blood clots. You may want to talk with your primary care physician if you have a history of stomach ulcers, allergies, blood clots, or bleeding disorders. Usually, patients will desire an aisle seat or a lay-flat seat for long distances during their initial recovery.
The answer varies from patient to patient, and whether you have surgery on the right leg or the left leg. As a general rule, you cannot drive if you are on narcotics or unsafe on the road. Patients on average are able to return to driving between 2 and 6 weeks after surgery. I usually advise my patients that if they feel like they wouldn’t be able to stop in the event of an emergency or if a pedestrian suddenly decided to cross the road in front of the car, they should not drive. Practice on a parking lot before driving on the road.
Robotic joint replacement can make bone cuts within 0.5mm of the plan and <1° of expected placement. In comparison, 15-20% of traditional instrumented knee replacements are unable to get within 3° of the expected resection.
Your surgeon is responsible for performing every aspect of the surgery. While the robot assists with improved data collection and bone cuts, the surgeon has to guide the instruments into the right place. The robot is incredibly accurate and prevents surgeons from cutting errors that are imperceptible to the human eye.
Robotic-assisted hip and knee surgery is a newer technology. Not all surgeons were trained in the robot during their training and are not comfortable with learning a new way to perform the same surgery.
Some joint replacement systems require special preoperative imaging (CT scan or x-rays). Dr. Morton does not require additional imaging beyond x-rays for his hip or knee replacement surgeries. During surgery two small incisions are made into your thigh and shin to place the robot trackers.
Pricing programs vary depending on the hospital, implant usage, and physician demand. While a robotic-assisted knee replacement requiring a CT-scan preoperatively will generally cost the hospital an additional $2,000 per patient as reported in some studies, the overall cost to the health system may be decreased due to lower complication rates.
Patients are not expected to pay any more for their robotic hip or knee replacement. Your bill will be the same from the hospital, regardless if you have a robotic-assisted, or traditional knee replacement.
Robotic assistance allows for more accurate placement of your implant, takes into account the positioning of your anatomy, and personalizing the implantation of your knee. Early and mid-term data from studies demonstrate that robotic-placed implants last longer, recover faster, and have lower amounts of pain overall.
This is a complex question depending on what job type you are doing.
Desk job: I tell most patients that they will feel well enough to begin working around two weeks after surgery. Some patients who are gung-ho will even start working immediately after surgery.
Light Labor: Light labor that requires frequent walking or light lifting. Some patients may require 6 weeks to 3 months before returning to work. Close monitoring will be needed to help you determine when you are safe.
Heavy labor: Construction and other types of manual labor usually requires at least 3 months of recovery. Some patients will have to change their careers depending on their demands. Talk with your surgeon before returning to work.
Custom implants and customized jigs are a technology that has not demonstrated to have brought significant value for patient outcomes. These devices have not been demonstrated to be more reliable than traditional knee replacements. It is likely because it does not take into account your soft-tissue anatomy at the time of surgery. This is the difference that robotic joint replacements provide.
Robotic joint replacements are a hot-topic in hip and knee replacements. While you may not need a robot to perform your surgery, robotic knee replacements are able to provide a much more accurate positioning of your knee replacements and personalize the implantation to your anatomy. Much like anterior hip replacements are able to position our implants better and improve outcomes, I believe that robotic joint replacements can make the same improvements for knee replacements.
Tobacco use is known to be a significant risk factor for loosening, infection, or wound healing problems. Minimizing your tobacco use or quitting before surgery will make a significant impact. If you are able to quit for life, you will significantly reduce your risk of other complications to your overall health as well. Learn more about tobacco effects on joint replacements here.
The arthritic pain from before surgery is usually removed following hip replacements. Many patients tell me they have minimal to no pain following surgery initially. Some patients have soreness for up to 2 months. Again, I have noticed that many patients have a lower amount of pain through the anterior approach.
Hip replacement recovery is variable. Many patients are feeling good at 6 weeks. It may take 3 months to a year before you completely recover from your hip replacement. The anterior hip replacement consistently allows for a quicker recovery.
Related Pages
Orthopedic Surgery for Patients from Australia and New Zealand
Orthopedic surgery is essential for many individuals with joint, bone, and muscle issues. For patients from Australia and New Zealand, seeking orthopedic surgery abroad can provide several advantages, including access to advanced treatment options, affordable [...]
Personalized Alignment In Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery has long been a solution for patients who have severe arthritis or joint degeneration. Traditionally, the procedure has involved using standardized techniques to position the knee implant. However, personalized alignment in knee [...]
Efficient Surgery: Improving Recovery Times for Patients
Recently, a significant focus has been on improving recovery times for patients undergoing surgery. Innovations in surgical techniques and technology are transforming surgeries, making them faster and more effective. Not only does this contribute [...]
Recalled Joint Implants: Essential Insights Patients Should Know
Joint replacements, such as knee, hip, and shoulder implants, have significantly enhanced the lives of individuals suffering from chronic pain and mobility limitations. However, despite their success, recalls do occur. These recalls can be [...]
Hiking After Knee Replacement: Tips for Staying Active
Knee replacement surgery can be life-changing, offering significant relief from pain and improved mobility. However, returning to physical activities like hiking may seem daunting for many. However, hiking after knee replacement is possible—and even beneficial [...]
Using PRP for Knee Arthritis: Essential Insights
Knee arthritis, a degenerative joint condition, affects millions worldwide, reducing mobility and quality of life. As patients explore alternatives to traditional treatments, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has gained traction as a promising intervention. This blog [...]







